Assay Development
Starting with your first assay, STATLIA MATRIX provides important tools to help you develop and then run your quantitation, potency bioassays, and immunogenicity tests.See your data in STATLIA MATRIX.
Start Collecting Important Information From Your First Assay
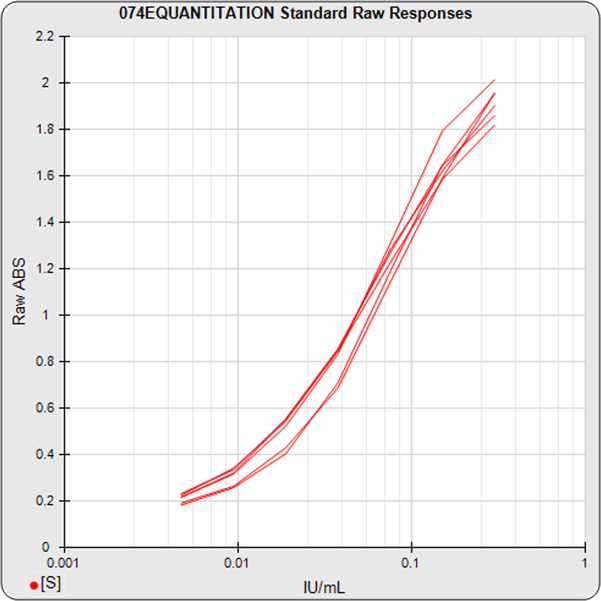
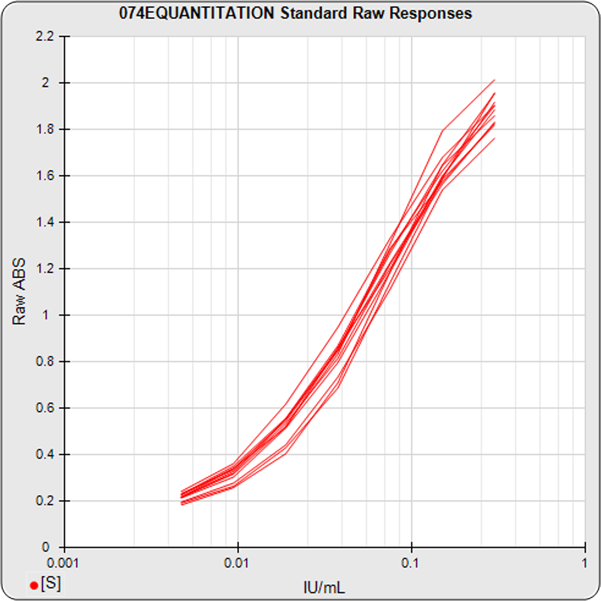
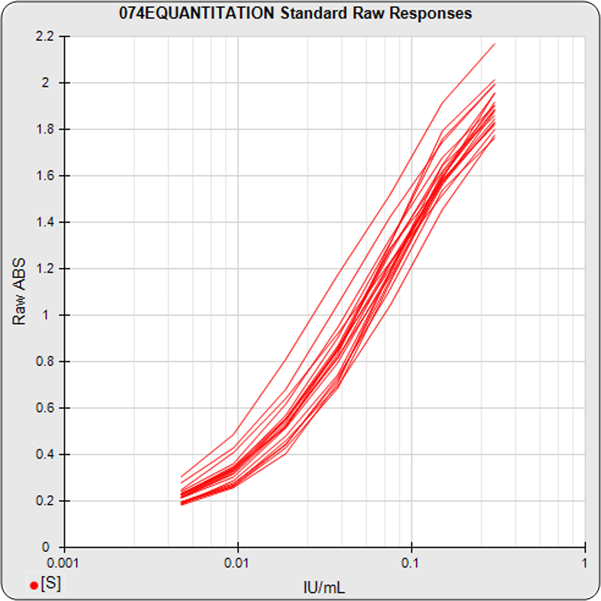
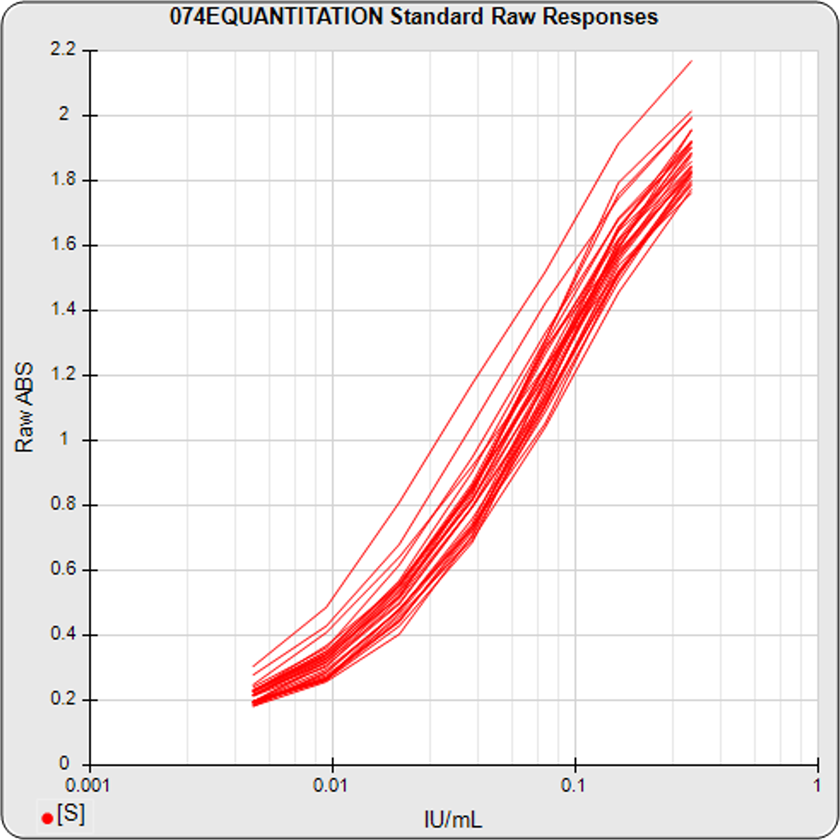
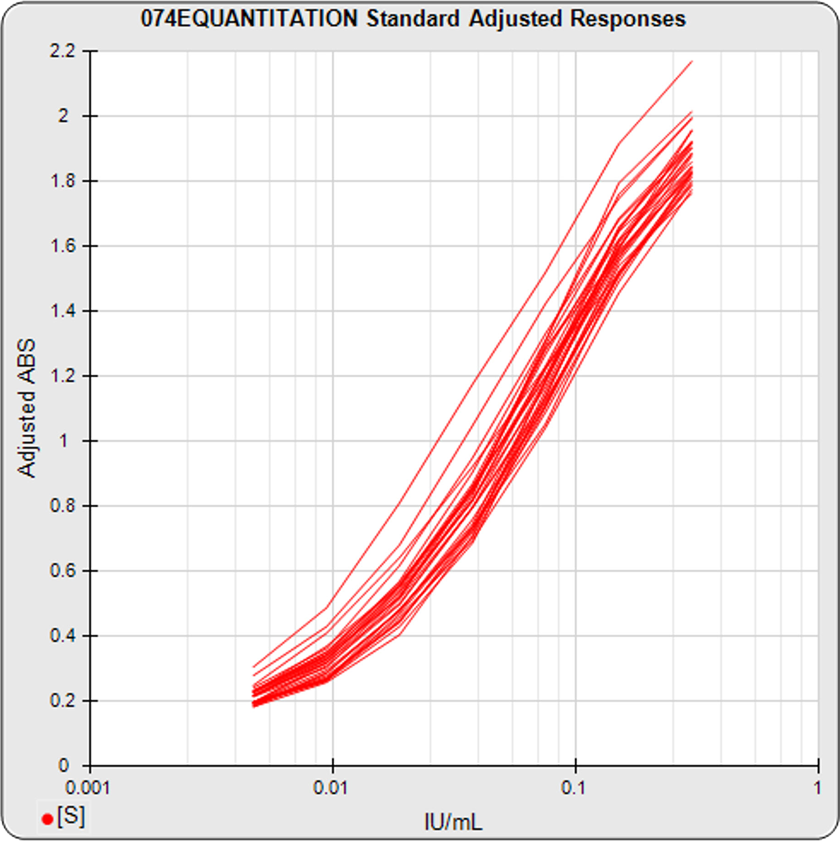
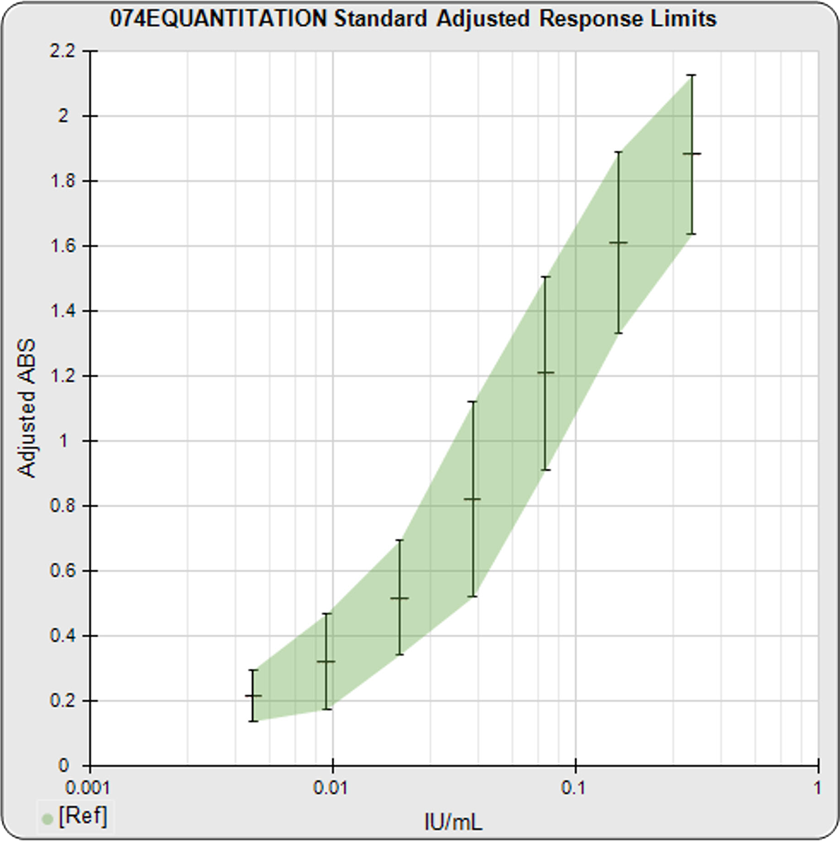
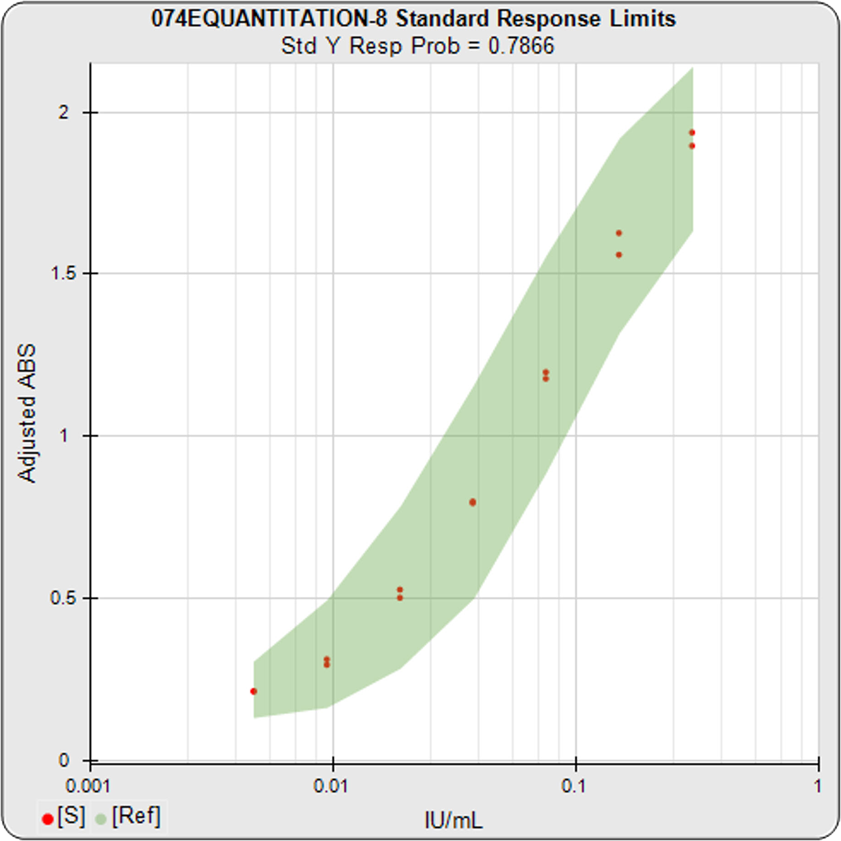
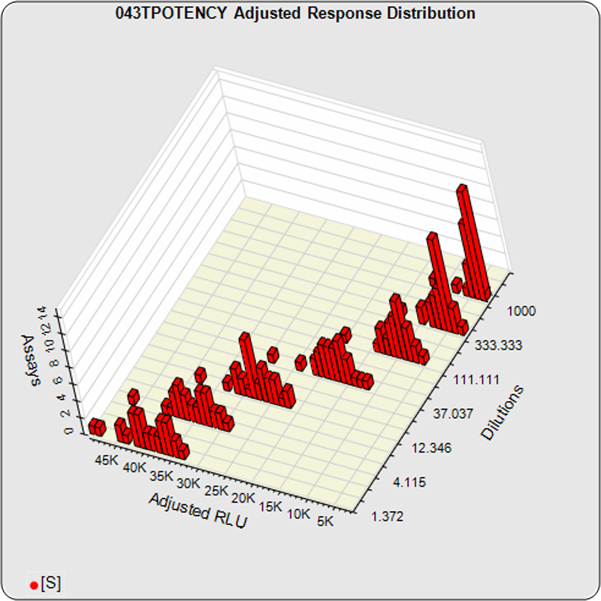
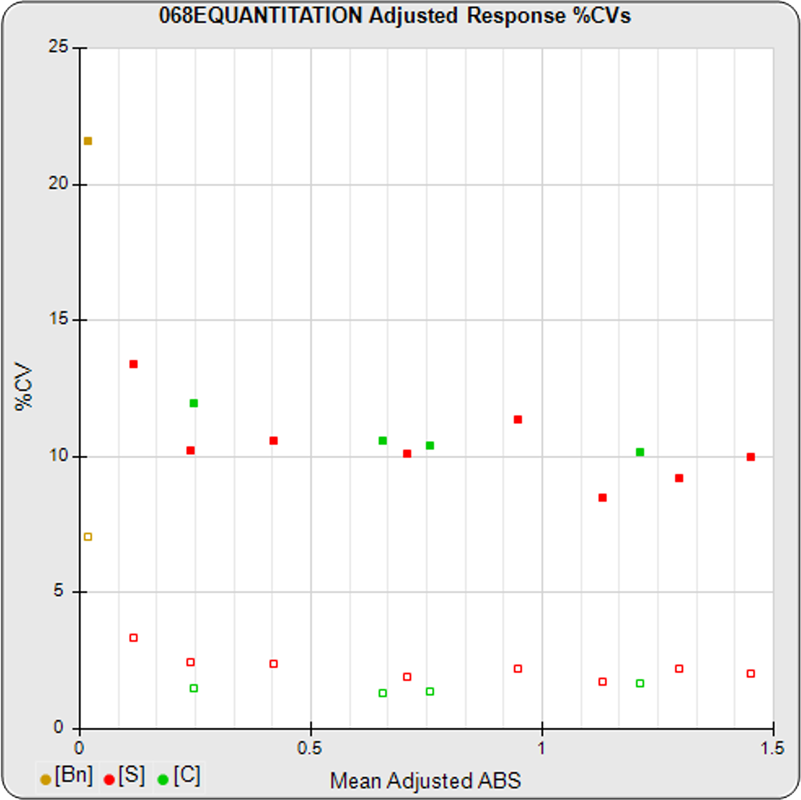
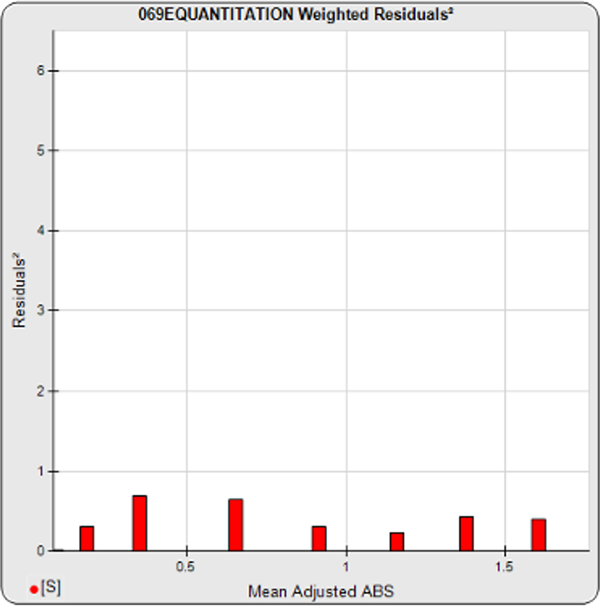
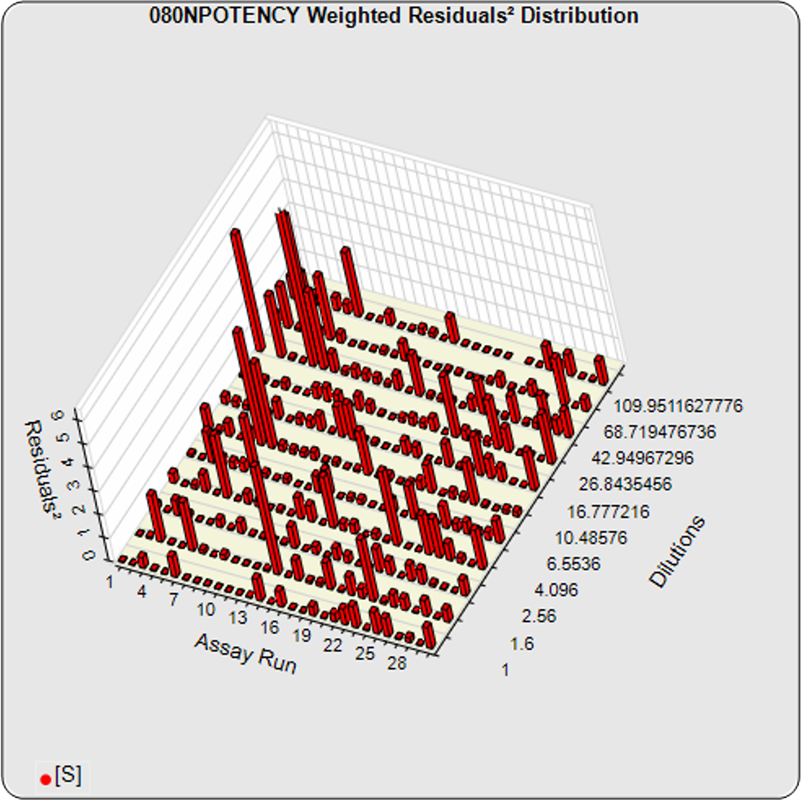
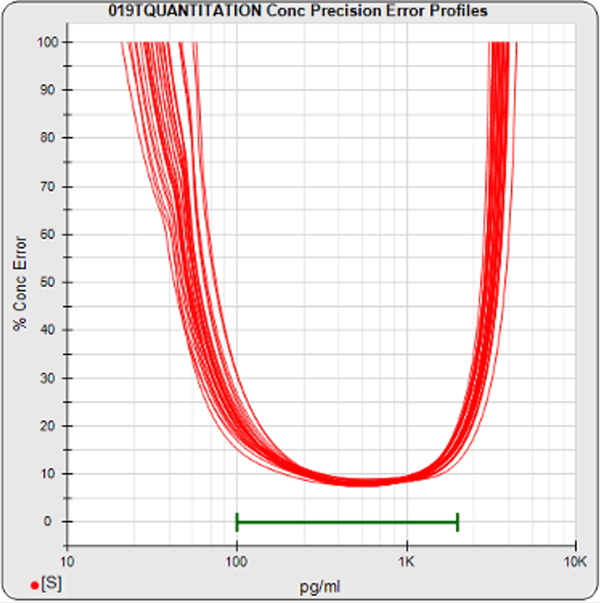
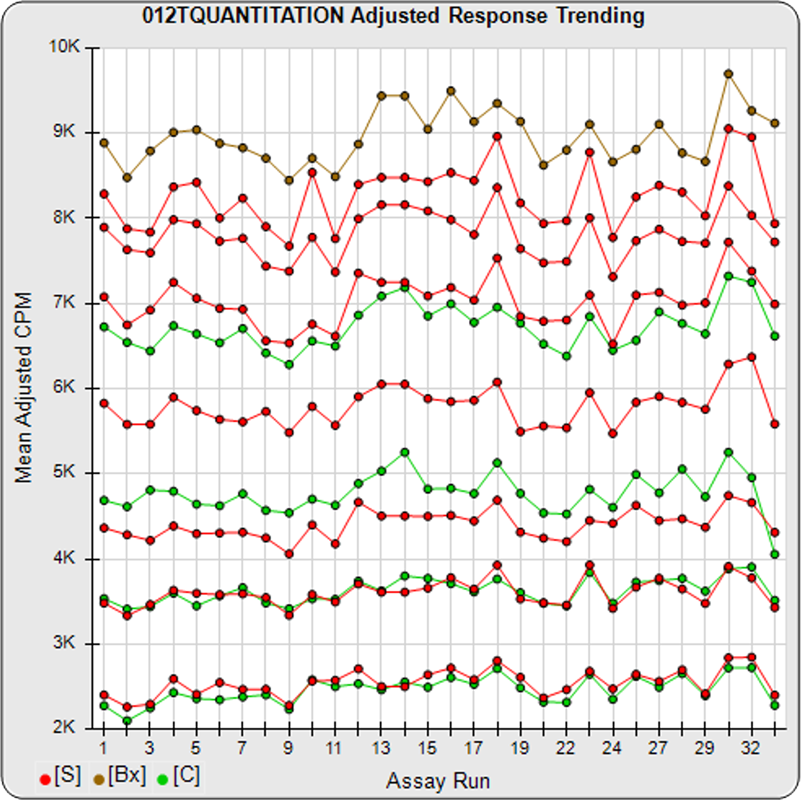
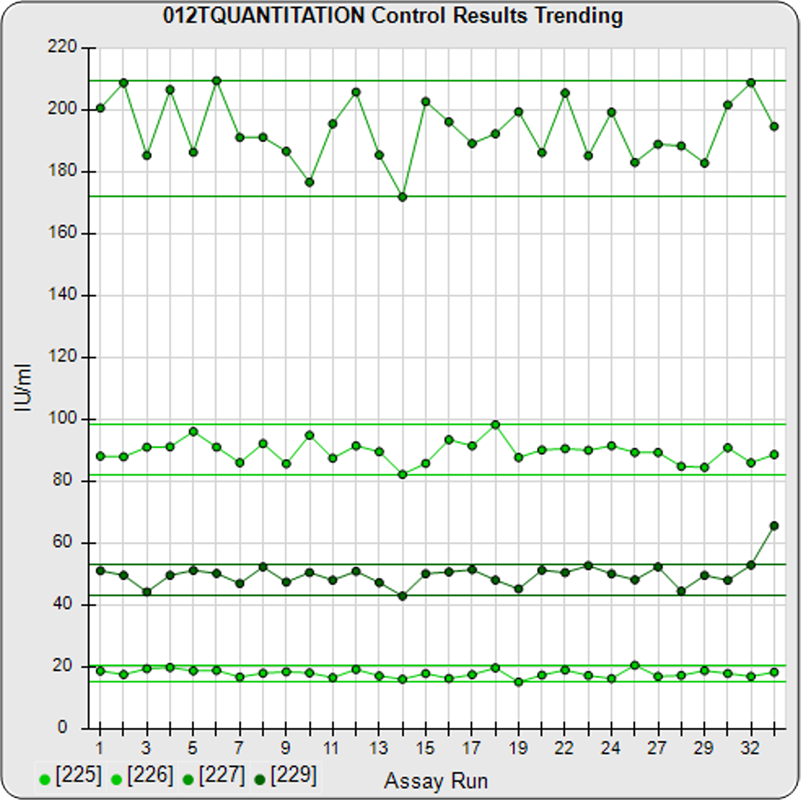
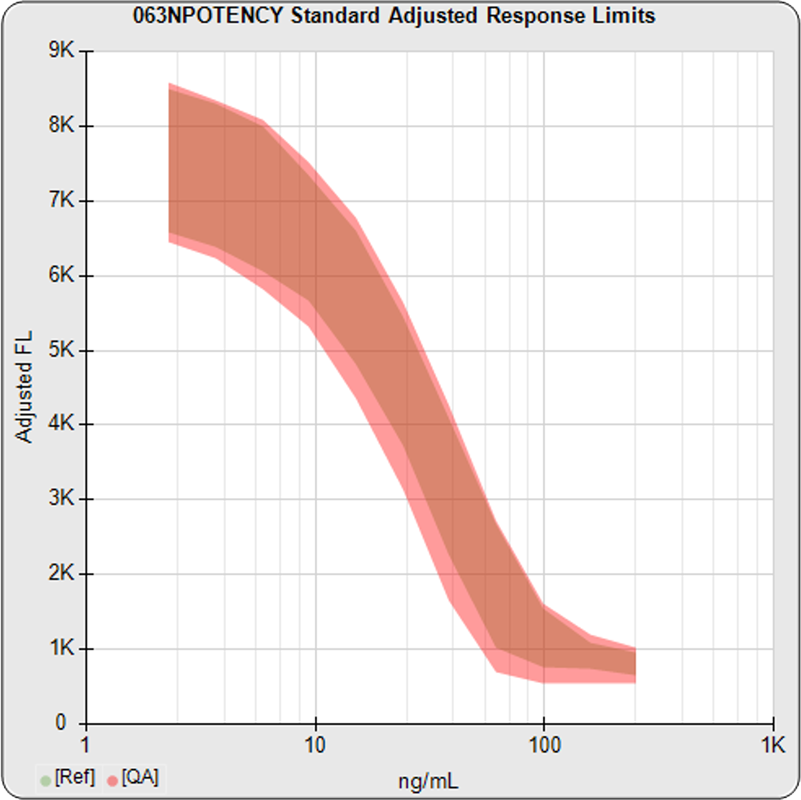
The informative graphs and tables start with your first assay. STATLIA MATRIX tracks important metrics such as optimal dilution doses, usable dose range, and if there is saturation of the reaction or signal at low and high dilutions.
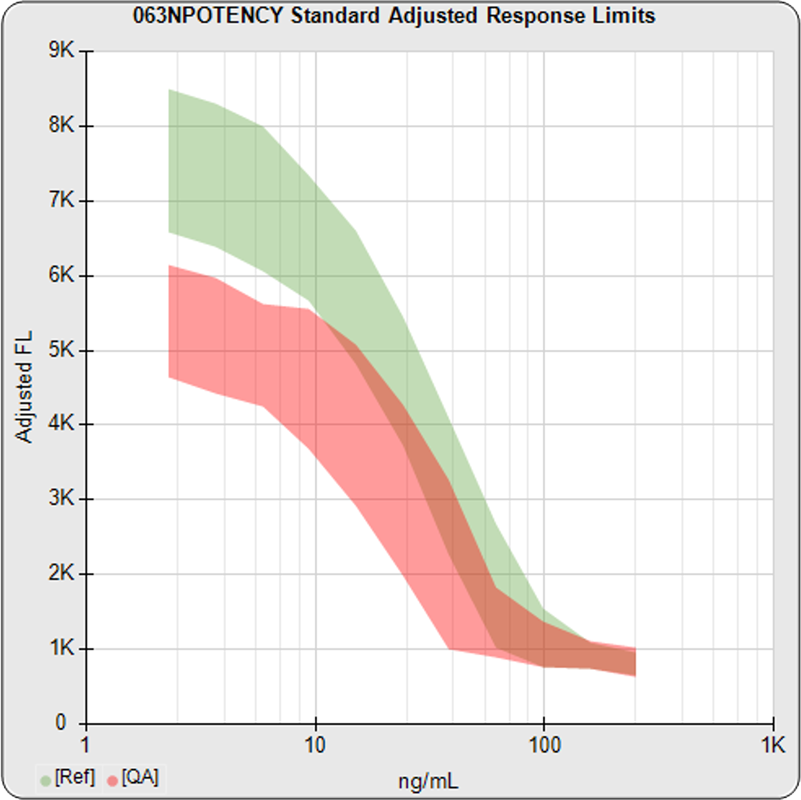
When you are developing or modifying a test protocol, STATLIA MATRIX uses the data in the program’s assay database to compare the effects of protocol changes to previous protocols so you can better evaluate those changes.
Reports are generated automatically that include graphs, metrics, ranges, acceptance limits, and more as you develop your test method. All development changes to test assays are tracked and saved.
With STATLIA MATRIX, you can see at a glance if your test method is ready for processing assays or if it needs further refinement.
As you run your assays, the software will automatically monitor any test behavior shift due to reagent lot changes or protocol differences.